Writing and Organizing Tests
What you'll learn
- How to organize your tests in Cypress and the types of supported files
- How to write tests in Cypress including hooks, exclusions, and configurations
- Test statuses and how to interpret them
- What files are automatically watched while writing Cypress tests
Folder structure
After adding a new project, Cypress will automatically scaffold out a suggested folder structure. By default it will create:
- JavaScript
- TypeScript
E2E:
/cypress.config.js
/cypress/fixtures/example.json
/cypress/support/commands.js
/cypress/support/e2e.js
Component:
/cypress.config.js
/cypress/fixtures/example.json
/cypress/support/commands.js
/cypress/support/component.js
/cypress/support/component-index.html
Both:
/cypress.config.js
/cypress/fixtures/example.json
/cypress/support/commands.js
/cypress/support/e2e.js
/cypress/support/component.js
/cypress/support/component-index.html
E2E:
/cypress.config.ts
/cypress/fixtures/example.json
/cypress/support/commands.ts
/cypress/support/e2e.ts
Component:
/cypress.config.ts
/cypress/fixtures/example.json
/cypress/support/commands.ts
/cypress/support/component.ts
/cypress/support/component-index.html
Both:
/cypress.config.ts
/cypress/fixtures/example.json
/cypress/support/commands.ts
/cypress/support/e2e.ts
/cypress/support/component.ts
/cypress/support/component-index.html
Configuring Folder Structure
While Cypress allows you to configure where your tests, fixtures, and support files are located, if you're starting your first project, we recommend you use the above structure.
You can modify the folder configuration in your configuration file. See the Cypress configuration for more detail.
Cypress may create
asset files in a
downloadsFolder, a
screenshotsFolder or a
videosFolder to store any downloads,
screenshots or videos created during the testing of your application.
Many users will opt to add these folders to their
.gitignore file (see below for an example).
Additionally, if you are storing sensitive variables in your
Cypress configuration these should also be ignored when you check into source control.
Spec files
Test files are located in cypress/e2e by default, but can be
configured to another
directory. Test files may be written as:
.js.jsx.ts.tsx.coffee.cjsx
Cypress also supports ES2015 out of the box. You can use either
ES2015 modules or CommonJS modules. This means you can import or require
both npm packages and local relative modules.
Check out our recipe using ES2015 and CommonJS modules.
To see an example of every command used in Cypress, open the
2-advanced-examples folder
within your cypress/e2e folder.
Fixture Files
Fixtures are used as external pieces of static data that can be used by your
tests. Fixture files are located in cypress/fixtures by default, but can be
configured to another
directory.
You would typically use them with the cy.fixture()
command and most often when you're stubbing
Network Requests.
Asset Files
There are some folders that may be generated after a test run, containing assets that were generated during the test run.
You may consider adding these folders to your .gitignore file to prevent checking files in these folders into source control, for example, using the default folder locations:
# Cypress asset folders to exclude from source control
cypress/downloads/
cypress/screenshots/
cypress/videos/
Download Files
Any files downloaded while testing an application's file download feature will
be stored in the downloadsFolder
which is set to cypress/downloads by default.
/cypress
/downloads
- records.csv
Screenshot Files
If screenshots were taken via the cy.screenshot()
command or automatically when a test fails, the screenshots are stored in the
screenshotsFolder which is set
to cypress/screenshots by default.
/cypress
/screenshots
/app.cy.js
- Navigates to main menu (failures).png
To learn more about screenshots and settings available, see Screenshots and Videos
Video Files
Any videos recorded of the run are stored in the
videosFolder which is set to
cypress/videos by default.
/cypress
/videos
- app.cy.js.mp4
Asset File Paths
Generated screenshots and videos are saved inside their respective folders
(cypress/screenshots, cypress/videos). The paths of the generated files will
be stripped of any common ancestor paths shared between all spec files found by
the specPattern option (or via the --spec command line option or spec
module API option, if specified)
Example 1:
- Spec file found
cypress/e2e/path/to/file/one.cy.js
- Common ancestor paths (calculated at runtime)
cypress/e2e/path/to/file
- Generated screenshot file
cypress/screenshots/one.cy.js/your-screenshot.png
- Generated video file
cypress/videos/one.cy.js.mp4
Example 2:
- Spec files found
cypress/e2e/path/to/file/one.cy.jscypress/e2e/path/to/two.cy.js
- Common ancestor paths (calculated at runtime)
cypress/e2e/path/to/
- Generated screenshot files
cypress/screenshots/file/one.cy.js/your-screenshot.pngcypress/screenshots/two.cy.js/your-screenshot.png
- Generated video files
cypress/videos/file/one.cy.js.mp4cypress/videos/two.cy.js.mp4
Assets in Cypress Cloud
Instead of administering assets yourself, you can save them to the cloud with Cypress Cloud.
Replay the test as it executed during the recorded run with full debug capability using Cypress Test Replay.
Screenshots and videos are stored permanently, attached to their respective test results, and easily shared or browsed through our web interface. To learn more about videos and settings available, see Screenshots and Videos.
Plugins file
The plugins file is a special file that executes in Node before the project is loaded, before the browser launches, and during your test execution. While the Cypress tests execute in the browser, the plugins file runs in the background Node process, giving your tests the ability to access the file system and the rest of the operating system by calling the cy.task() command.
The plugins file is a good place to define how you want to bundle the spec files via the preprocessors, how to find and launch the browsers via the browser launch API, and other cool things. Read our plugins guide for more details and examples.
The initial imported plugins file can be configured to another file.
Support file
To include code before your test files, set the
supportFile
path. By default,
supportFile
is set to look for one of the following files:
Component:
cypress/support/component.jscypress/support/component.jsxcypress/support/component.tscypress/support/component.tsx
E2E:
cypress/support/e2e.jscypress/support/e2e.jsxcypress/support/e2e.tscypress/support/e2e.tsx
For a given testing type, multiple matching
supportFile files will result in an error when Cypress loads.
supportFile per testing type
Depending on which testing type you are
using, you can configure your supportFile accordingly.
Cypress automatically creates an example support file for each configured testing type, which has several commented out examples.
This file runs before every single spec file. We do this purely as a convenience mechanism so you don't have to import this file.
By default Cypress will automatically include type-specific support files. For
E2E, the default is cypress/support/e2e.{js,jsx,ts,tsx}, and for Component
Testing cypress/support/component.{js,jsx,ts,tsx}.
The support file is a great place to put reusable behavior such as custom commands or global overrides that you want applied and available to all of your spec files.
The initial imported support file can be configured to another file or turned
off completely using the
supportFile configuration.
From your support file you can import or require other files to keep things
organized.
You can define behaviors in a before or beforeEach within any of the
cypress/support files:
beforeEach(() => {
cy.log('I run before every test in every spec file!!!!!!')
})
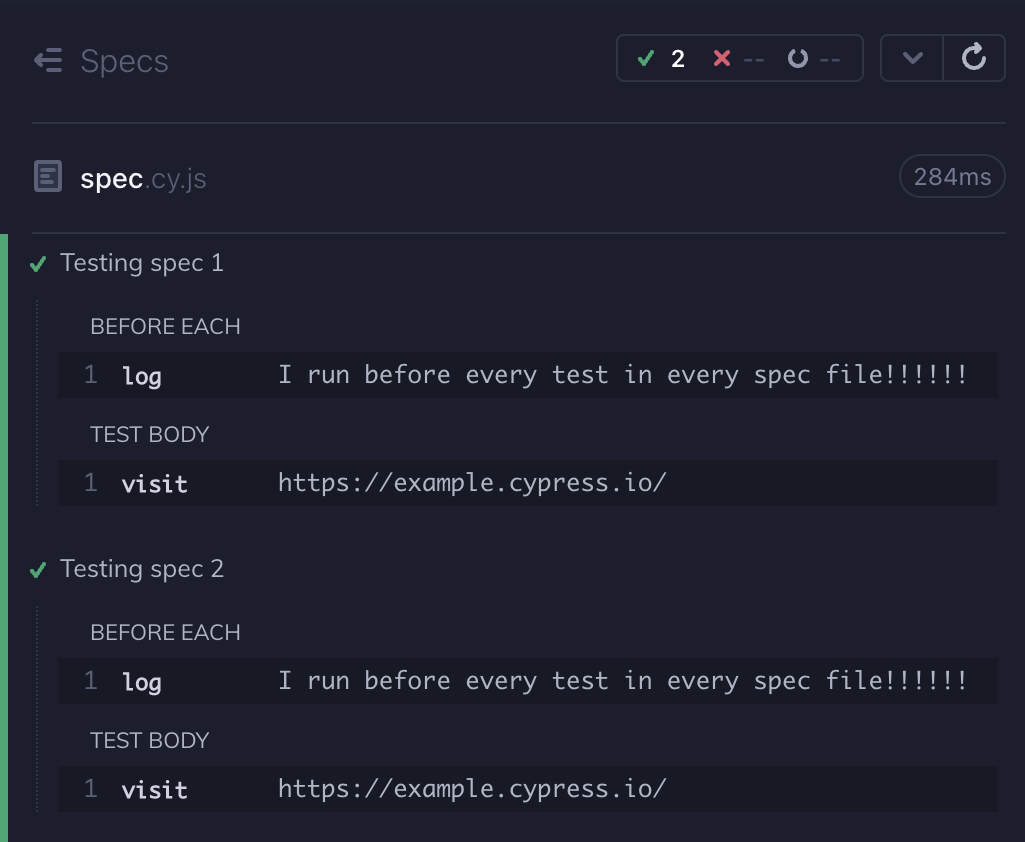
Note: This example assumes you are already familiar with Mocha hooks.
Execution
Cypress executes the support file before the spec file. For example, when
Cypress executes a spec file via cypress open or cypress run, it executes
the files in the following order:
e2e example:
support/e2e.js(your support file)e2e/spec-a.cy.js(your spec file)
component example:
support/component.js(your support file)components/Button/Button.cy.js(your spec file)
Troubleshooting
If Cypress does not find the spec files for some reason, you can troubleshoot its logic by opening or running Cypress with debug logs enabled:
DEBUG=cypress:cli,cypress:data-context:sources:FileDataSource,cypress:data-context:sources:ProjectDataSource npx cypress open
## or
DEBUG=cypress:cli,cypress:data-context:sources:FileDataSource,cypress:data-context:sources:ProjectDataSource npx cypress run
Writing tests
Cypress is built on top of Mocha
and Chai. We support both Chai's
BDD and TDD assertion styles. Tests you write in Cypress will mostly adhere
to this style.
If you're familiar with writing tests in JavaScript, then writing tests in Cypress will be a breeze.
To start writing tests for your app, follow our guides for writing your first Component or End-to-End test.
Needing a low code approach to create tests? Use Cypress Studio to record your browser interactions.
Test Structure
The test interface, borrowed from
Mocha, provides describe(),
context(), it() and specify().
context() is identical to describe() and specify() is identical to it(),
so choose whatever terminology works best for you.
// -- Start: Our Application Code --
function add(a, b) {
return a + b
}
function subtract(a, b) {
return a - b
}
function divide(a, b) {
return a / b
}
function multiply(a, b) {
return a * b
}
// -- End: Our Application Code --
// -- Start: Our Cypress Tests --
describe('Unit test our math functions', () => {
context('math', () => {
it('can add numbers', () => {
expect(add(1, 2)).to.eq(3)
})
it('can subtract numbers', () => {
expect(subtract(5, 12)).to.eq(-7)
})
specify('can divide numbers', () => {
expect(divide(27, 9)).to.eq(3)
})
specify('can multiply numbers', () => {
expect(multiply(5, 4)).to.eq(20)
})
})
})
// -- End: Our Cypress Tests --
Hooks
Cypress also provides hooks (borrowed from Mocha).
These are helpful to set conditions that you want to run before a set of tests or before each test. They're also helpful to clean up conditions after a set of tests or after each test.
before(() => {
// root-level hook
// runs once before all tests
})
beforeEach(() => {
// root-level hook
// runs before every test block
})
afterEach(() => {
// runs after each test block
})
after(() => {
// runs once all tests are done
})
describe('Hooks', () => {
before(() => {
// runs once before all tests in the block
})
beforeEach(() => {
// runs before each test in the block
})
afterEach(() => {
// runs after each test in the block
})
after(() => {
// runs once after all tests in the block
})
})
The order of hook and test execution is as follows:
- All
before()hooks run (once) - Any
beforeEach()hooks run - Tests run
- Any
afterEach()hooks run - All
after()hooks run (once)
🚨 Before writing after() or afterEach() hooks, please see our
thoughts on the anti-pattern of cleaning up state with after() or afterEach().
Excluding and Including Tests
To run a specified suite or test, append .only to the function. All nested
suites will also be executed. This gives us the ability to run one test at a
time and is the recommended way to write a test suite.
// -- Start: Our Application Code --
function fizzbuzz(num) {
if (num % 3 === 0 && num % 5 === 0) {
return 'fizzbuzz'
}
if (num % 3 === 0) {
return 'fizz'
}
if (num % 5 === 0) {
return 'buzz'
}
}
// -- End: Our Application Code --
// -- Start: Our Cypress Tests --
describe('Unit Test FizzBuzz', () => {
function numsExpectedToEq(arr, expected) {
// loop through the array of nums and make
// sure they equal what is expected
arr.forEach((num) => {
expect(fizzbuzz(num)).to.eq(expected)
})
}
// only run this test
it.only('returns "fizz" when number is multiple of 3', () => {
numsExpectedToEq([9, 12, 18], 'fizz')
})
it('returns "buzz" when number is multiple of 5', () => {
numsExpectedToEq([10, 20, 25], 'buzz')
})
it('returns "fizzbuzz" when number is multiple of both 3 and 5', () => {
numsExpectedToEq([15, 30, 60], 'fizzbuzz')
})
})
To skip a specified suite or test, append .skip() to the function. All nested
suites will also be skipped.
it.skip('returns "fizz" when number is multiple of 3', () => {
numsExpectedToEq([9, 12, 18], 'fizz')
})
Test Isolation
Best Practice: Tests should always be able to be run independently from one another and still pass.
As stated in our mission, we hold ourselves accountable to champion a testing process that actually works, and have built Cypress to guide developers towards writing independent tests from the start.
We do this by cleaning up test state and the browser context before each test to ensure that the operation of one test does not affect another test later on. The goal for each test should be to reliably pass whether run in isolation or consecutively with other tests. Having tests that depend on the state of an earlier test can potentially cause nondeterministic test failures which makes debugging challenging.
The behavior of running tests in a clean browser context is described as
testIsolation.
The test isolation is a global configuration and can be overridden for
end-to-end testing at the describe level with the
testIsolation option.
To learn more about this behavior and the trade-offs of disabling it, review our Test Isolation guide.
Test Configuration
It is possible to apply test configuration values to a suite or test. Pass a configuration object to the test or suite function as the second argument.
This configuration will take effect during the suite or tests where they are set then return to their previous default values after the suite or tests are complete.
Syntax
describe(name, config, fn)
context(name, config, fn)
it(name, config, fn)
specify(name, config, fn)
Allowed config values
Note: Some configuration values are readonly and cannot be changed via test configuration. Be sure to review the list of test configuration options.
Suite configuration
If you want to target a suite of tests to run or be excluded when run in a
specific browser, you can override the browser configuration within the suite
configuration. The browser option accepts the same arguments as
Cypress.isBrowser().
The following suite of tests will be skipped if running tests in Chrome browsers.
describe('When NOT in Chrome', { browser: '!chrome' }, () => {
it('Shows warning', () => {
cy.get('[data-testid="browser-warning"]').should(
'contain',
'For optimal viewing, use Chrome browser'
)
})
it('Links to browser compatibility doc', () => {
cy.get('a.browser-compat')
.should('have.attr', 'href')
.and('include', 'browser-compatibility')
})
})
The following suite of tests will only execute when running in the Firefox browser. Additionally, it will overwrite the viewport resolution.
describe(
'When in Firefox',
{
browser: 'firefox',
viewportWidth: 1024,
viewportHeight: 700,
},
() => {
it('Sets the expected viewport and API URL', () => {
expect(cy.config('viewportWidth')).to.equal(1024)
expect(cy.config('viewportHeight')).to.equal(700)
})
}
)
Single test configuration
You can configure the number of retry attempts during cypress run or
cypress open. See Test Retries for more
information.
it('should redirect unauthenticated user to sign-in page', {
retries: {
runMode: 3,
openMode: 2
}
} () => {
// test code...
})
})
Dynamically Generate Tests
You can dynamically generate tests using JavaScript.
describe('if your app uses jQuery', () => {
;['mouseover', 'mouseout', 'mouseenter', 'mouseleave'].forEach((event) => {
it('triggers event: ' + event, () => {
// if your app uses jQuery, then we can trigger a jQuery
// event that causes the event callback to fire
cy.get('#with-jquery')
.invoke('trigger', event)
.get('[data-testid="messages"]')
.should('contain', 'the event ' + event + 'was fired')
})
})
})
The code above will produce a suite with 4 tests:
> if your app uses jQuery
> triggers event: 'mouseover'
> triggers event: 'mouseout'
> triggers event: 'mouseenter'
> triggers event: 'mouseleave'
Assertion Styles
Cypress supports both BDD (expect/should) and TDD (assert) style plain
assertions. Read more about plain assertions.
it('can add numbers', () => {
expect(add(1, 2)).to.eq(3)
})
it('can subtract numbers', () => {
assert.equal(subtract(5, 12), -7, 'these numbers are equal')
})
The .should() command and its alias .and() can also be used to more easily chain assertions off of Cypress commands. Read more about assertions.
cy.wrap(add(1, 2)).should('equal', 3)
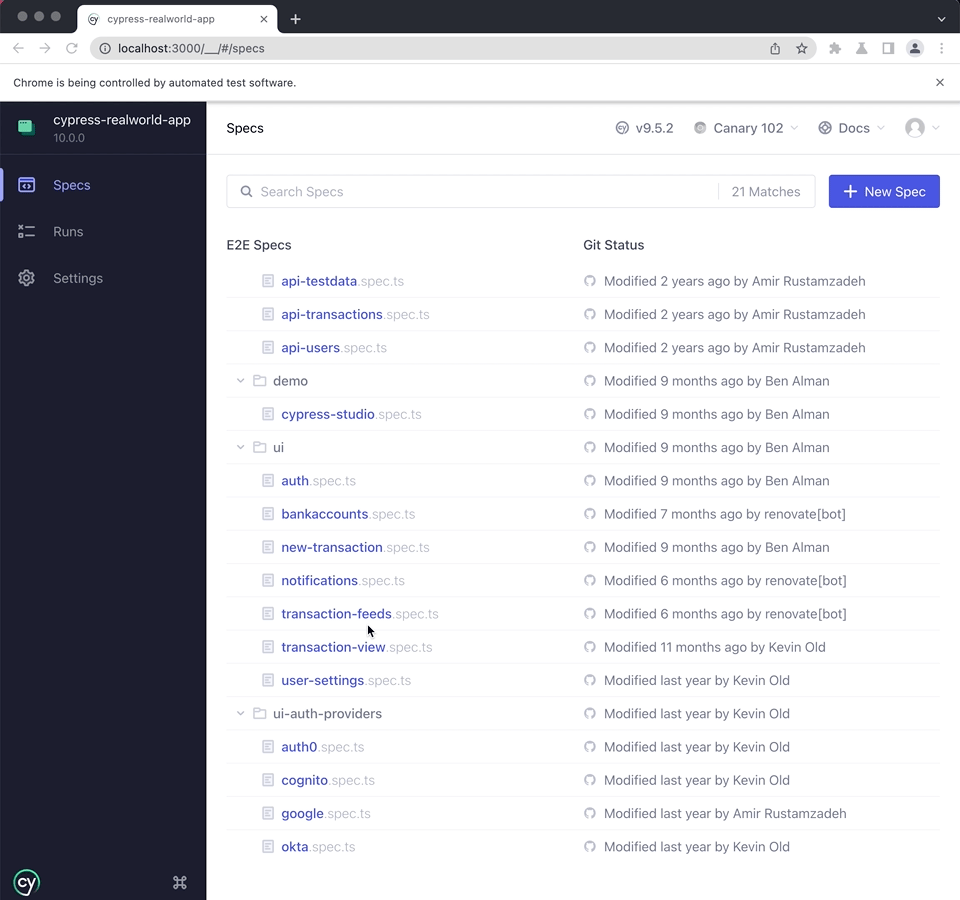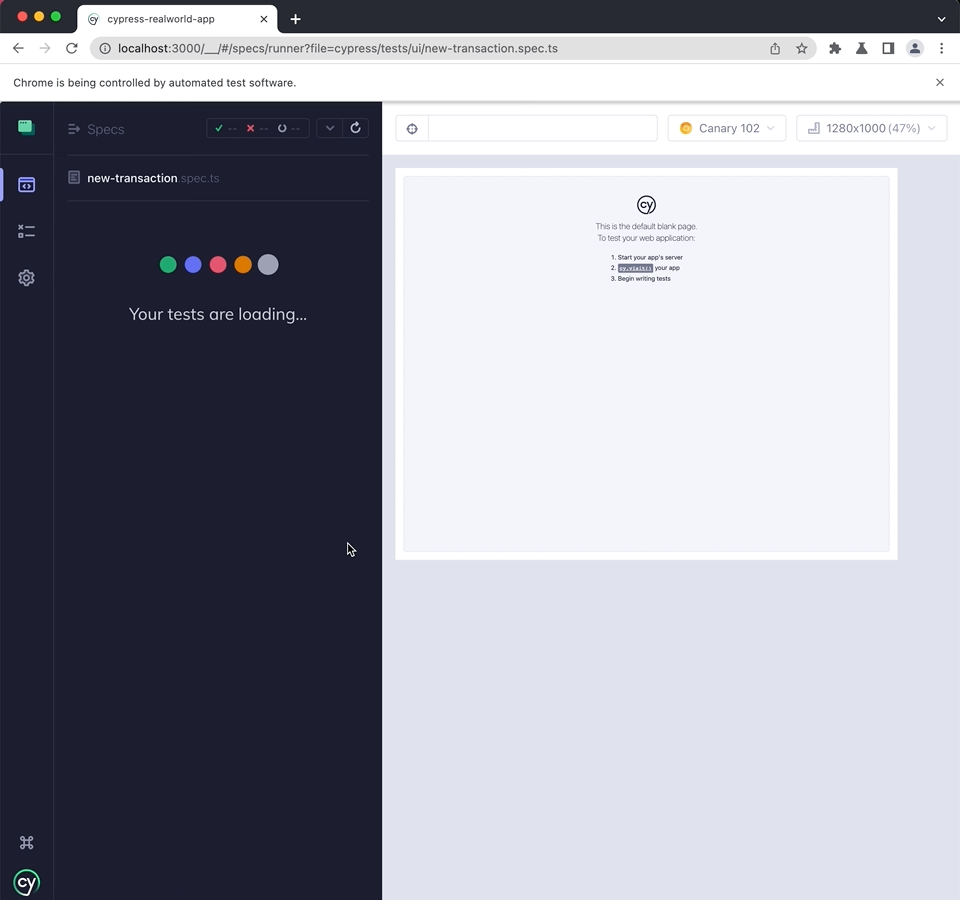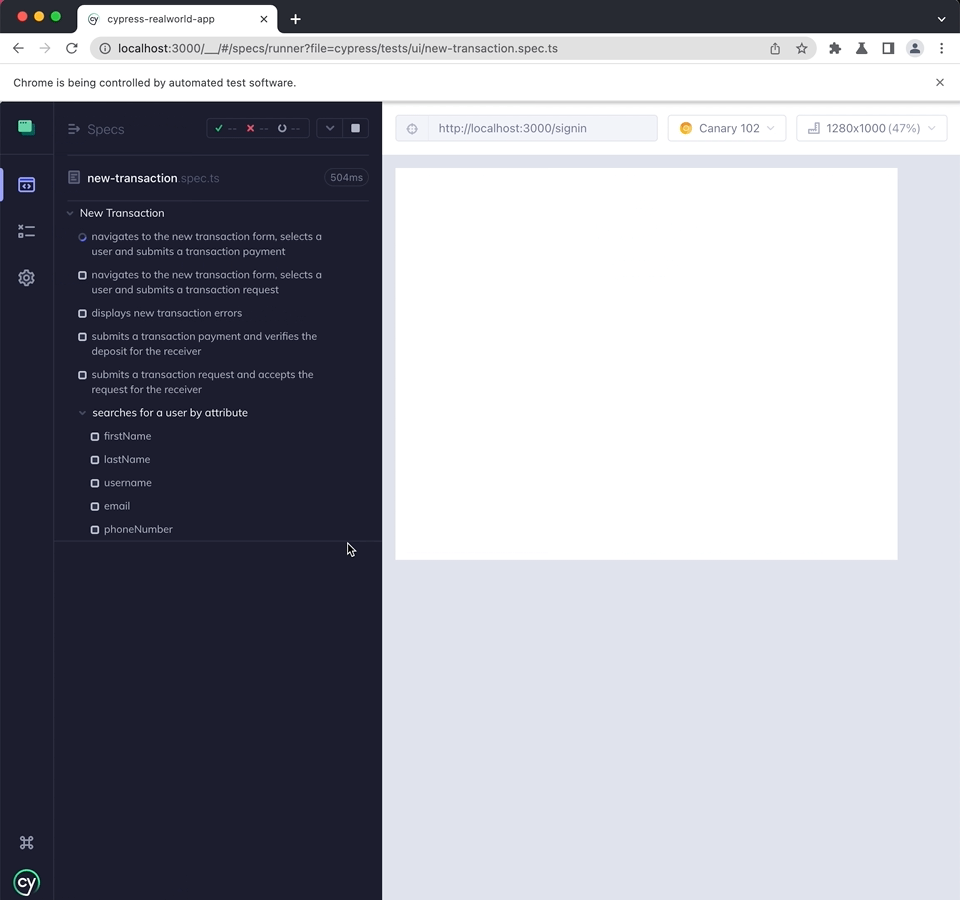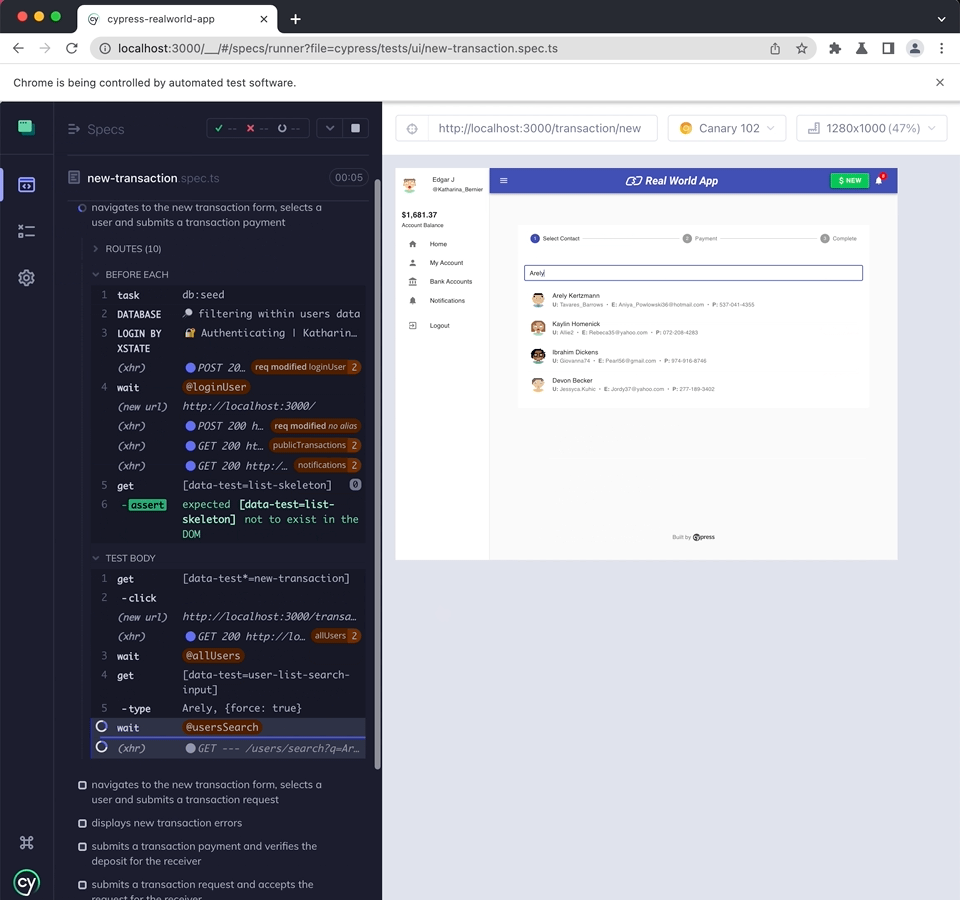
Running tests
You can run a test by clicking on the spec filename. For example the Cypress RealWorld App has multiple test files, but below we run the "new-transaction.spec.ts" test file by clicking on it.
Test statuses
After the Cypress spec completes every test has one of four statuses: passed, failed, pending, or skipped. The behavior of these statuses are inherited from the Mocha, since this is the test runner leveraged by Cypress.
Passed
Passed tests have successfully completed all their hooks and commands without failing any assertions. The test screenshot below shows a passed test:
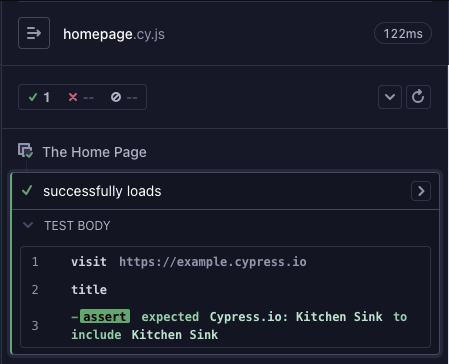
Note that a test can pass after several test retries. In that case the Command Log shows some failed attempts, but ultimately the entire test finishes successfully.
Failed
Good news - the failed hook or test has found a problem. Could be much worse - it could be a user hitting this bug!
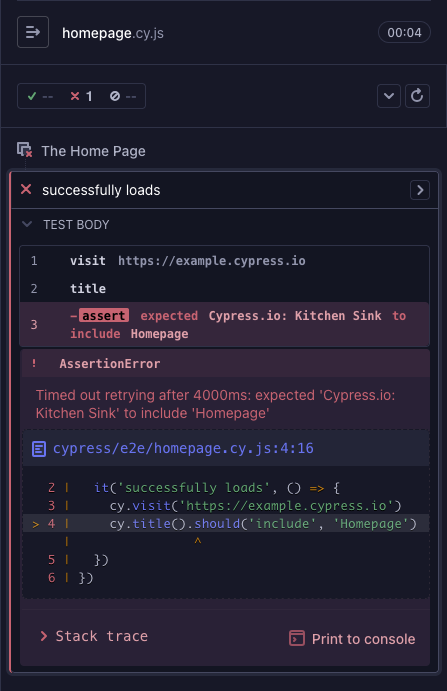
After a test fails, the Test Replay or screenshots and videos with Cypress Cloud can help find the problem so it can be fixed.
Pending
You can write placeholder tests in several ways as shown below, and Cypress knows NOT to run them. Additionally, you can conditionally specify which browser(s) and tests should run, including if the test should not run for the browser currently being tested, it is marked as pending.
Cypress marks all the tests below as pending.
describe('TodoMVC', () => {
it('is not written yet')
it.skip('adds 2 todos', function () {
cy.visit('/')
cy.get('[data-testid="new-todo"]').as('new').type('learn testing{enter}')
cy.get('@new').type('be cool{enter}')
cy.get('[data-testid="todo-list"] li').should('have.length', 100)
})
xit('another test', () => {
expect(false).to.true
})
it('only test chrome', { browser: 'chrome' }, () => {
cy.visit('/')
cy.contains('To Do')
})
})
All four tests above are marked pending when Cypress finishes running the spec file.
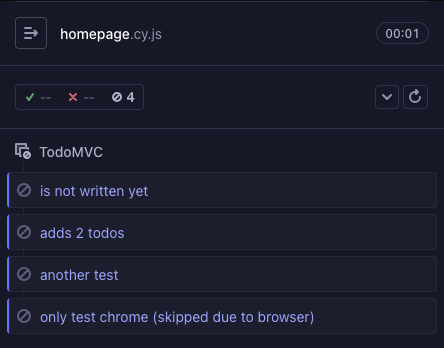
So remember - if you (the test writer) knowingly skip a test using one of the above three ways, Cypress counts it as a pending test.
Skipped
The last test status is for tests that you meant to run, but these tests were
skipped due to some run-time error. For example, imagine a group of tests
sharing the same beforeEach hook - where you visit the page in the
beforeEach hook.
If a command inside the beforeEach hook fails - for example, if we want to visit a non-existent page /does-not-exist instead of the / - and we change our beforeEach to fail:
beforeEach(() => {
cy.visit('/does-not-exist')
})
When Cypress starts executing the first test, the beforeEach hook fails. Now
the first test is marked as failed. BUT if the beforeEach hook failed
once, why would we execute it again before the second test? It would just fail
the same way! So Cypress skips the remaining tests in that block, because they
would also fail due to the beforeEach hook failure.
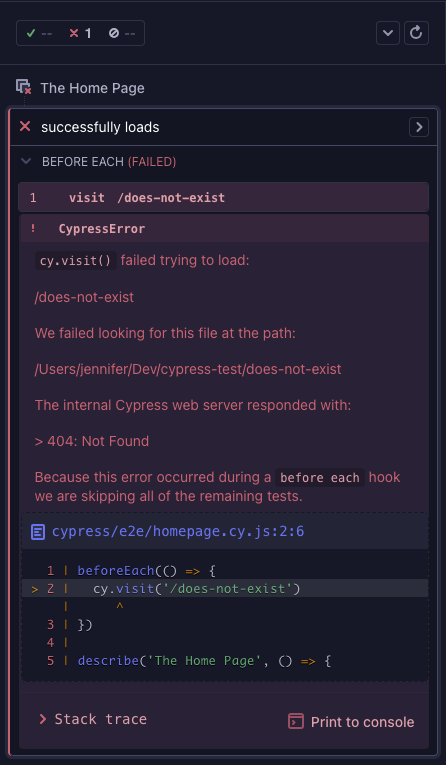
If we collapse the test commands, we can see the empty box marking the skipped test "adds 2 todos".
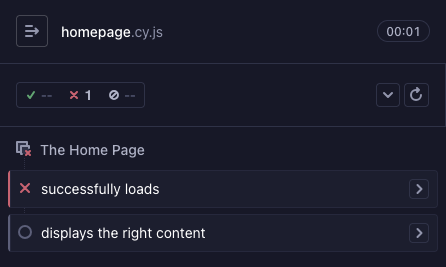
The tests that were meant to be executed but were skipped due to some run-time
problem are marked "skipped" by Cypress. This is typically observed when a
before, beforeEach or afterEach hook fails.
Watching tests
When running in using cypress open, Cypress watches the filesystem for changes to your spec files. Soon after adding or updating a test Cypress will reload it and run all of the tests in that spec file.
This makes for a productive development experience because you can add and edit tests as you're implementing a feature and the Cypress user interface will always reflect the results of your latest edits.
Remember to use
.only
to limit which tests are run: this can be especially useful when you've got a
lot of tests in a single spec file that you're constantly editing; consider also
splitting your tests into smaller files each dealing with logically related
behavior.
What is watched?
Files
Folders
- E2E directory (
cypress/e2e/by default) - Support directory (
cypress/support/by default)
The folder, the files within the folder, and all child folders and their files (recursively) are watched.
Those folder paths refer to the default folder paths. If you've configured Cypress to use different folder paths then the folders specific to your configuration will be watched.
What isn't watched?
Everything else; this includes, but isn't limited to, the following:
- Your application code
node_modulescypress/fixtures/
If you're developing using a modern JS-based web application stack then you've likely got support for some form of hot module replacement which is responsible for watching your application code—HTML, CSS, JS, etc.—and transparently reloading your application in response to changes.
Configuration
Set the watchForFileChanges
configuration property to false to disable file watching.
Nothing is watched during cypress run.
The watchForFileChanges property is only in effect when running Cypress using
cypress open.
The component responsible for the file-watching behavior in Cypress is the
webpack-preprocessor.
This is the default file-watcher packaged with Cypress.
If you need further control of the file-watching behavior you can configure this preprocessor explicitly: it exposes options that allow you to configure behavior such as what is watched and the delay before emitting an "update" event after a change.
Cypress also ships other file-watching preprocessors - you'll have to configure these explicitly if you want to use them.