Troubleshooting
What you'll learn
- Resources to help you troubleshoot Cypress App issues
- Common steps to isolate and resolve problems
Start here
There are times when you will encounter errors or unexpected behavior with Cypress itself. This guide recommends some resources and steps to take to troubleshoot those problems.
Update Cypress
We always recommend using the latest version of the Cypress App. If you're not using the latest version, upgrade to the latest version. Your issue may already be resolved.
Support channels
Check these support resources for Cypress App issues:
- Connect with our community in Discord
- Search existing GitHub issues
- Search this documentation (search is in the top right) 😉
- Search Stack Overflow for relevant answers
- If you still haven't found a solution, open an issue with a reproducible example.
If your organization signs up for one of our paid plans, you can get dedicated email support, which gives you one-on-one help from our team.
Isolate the Problem
When debugging a failing test, follow these general principles to isolate the problem:
- Look at the screenshots, video, or Test Replay of the test. Test Replay will show you the exact steps that were taken during the test including console logs and requests.
- Split large spec files into smaller ones.
- Split long tests into smaller tests.
- Run the same test in different browsers to isolate the problem to a specific browser.
- Run the same test in different environments (local, CI, etc.) to isolate the problem to a specific environment.
- Reduce the test to the smallest possible test that still reproduces the problem.
Troubleshooting Steps
Below are some steps you can take to troubleshoot common issues with Cypress.
Clear Cypress cache
If you're having an issue during installation of Cypress, try removing the contents of the Cypress cache.
This will clear out all installed versions of Cypress that may be cached on your machine.
cypress cache clear
After running this command, you will need to run cypress install before
running Cypress again.
- npm
- yarn
- pnpm
npm install cypress --save-dev
yarn add cypress --dev
pnpm add --save-dev cypress
Allow the Cypress Chrome extension
Cypress utilizes a Chrome extension in order to run properly. If you or your company block specific Chrome extensions, this may cause problems with running Cypress. You will want to ask your administrator to allow the Cypress extension ID below:
caljajdfkjjjdehjdoimjkkakekklcck
You can check the current company policies for your Chrome installation by typing chrome://policy into the address bar and pressing Enter.
Allow Cypress URLs on VPNs
To send the data and results of your tests to Cypress Cloud, Cypress needs free access to some URLs.
If you are running the tests from within a restrictive VPN you will need to allow some URLs so that Cypress can have effective communication with Cypress Cloud.
The URLs are the following:
https://api.cypress.io- Cypress API, Studio, cy.prompt()https://assets.cypress.io- Asset CDN (Org logos, icons, videos, screenshots, etc.)https://authenticate.cypress.io- Authentication APIhttps://capture.cypress.io- Cypress Test Replayhttps://s3.amazonaws.com/capture.cypress.io- Uploading Cypress Test Replay from Test Runnerhttps://cloud.cypress.io- Cypress Cloud, Studiohttps://docs.cypress.io- Cypress documentationhttps://download.cypress.io- CDN download of Cypress binaryhttps://on.cypress.io- URL shortener for link redirects
If you are using GitHub Enterprise or GitLab for Enterprise (Self-managed), you may also need to add the following to the version control IP allowlist:
3.211.102.119- Dedicated IP18.213.72.78- Dedicated IP35.169.145.173- Dedicated IP44.199.152.70- Dedicated IP52.70.95.89- Dedicated IP
Clear App Data
Cypress maintains some local application data in order to save user preferences and more quickly start up. Sometimes this data can become corrupted. You may fix an issue you have by clearing this app data.
To clear App Data
- Open Cypress via
cypress open - Go to
Developer Tools->View App Data - This will take you to the directory in your file system where your App Data
is stored. If you cannot open Cypress, search your file system for a
directory named
cywhose content should look something like this:
📂 production
📄 all.log
📁 browsers
📁 bundles
📄 cache
📁 projects
📁 proxy
📄 state.json
- Delete everything in the
cyfolder - Close Cypress and open it up again
Print DEBUG logs
Cypress utilizes the debug module.
That means you can receive helpful debugging output by running Cypress with a system-level environment variable DEBUG set to cypress:* prior to running cypress run or cypress open.
Enabling debug output can generate a large amount of data. This may also impact performance. Only enable debug output when you need it.
To reduce the amount of debug output data generated, replace cypress:* using a more selective value for DEBUG.
See below, including the section Log sources.
If you need to share debug output collected in a file, consider first compressing it with a ZIP utility or similar to reduce the file size before sharing.
On macOS, Linux or Windows (Git Bash):
- npm
- Yarn
- pnpm
DEBUG=cypress:* npx cypress run
DEBUG=cypress:* yarn cypress run
DEBUG=cypress:* pnpm cypress run
You can change run to open in the above to capture debug logs when starting your tests from the Cypress Specs UI.
For non-POSIX type shells on Windows, set the DEBUG environment variable as follows. (Replace npx with yarn or pnpm if you are using Yarn or pnpm package managers instead of npm.)
On Windows CMD:
set DEBUG=cypress:*
npx cypress run
On Windows PowerShell:
$env:DEBUG='cypress:*'
npx cypress run
If you have issues with the logs not printing, it may be a permissions issue with setting the environment variable in your terminal. You may need to run your terminal in administrative mode or review your permission settings.
How to run Cypress CLI commands provides background information on running Cypress from the command line and includes a reference of additional command line options.
Detailed Logs
There are several levels of DEBUG messages
## prints very few top-level messages
DEBUG=cypress:server ...
## prints ALL messages from server package
DEBUG=cypress:server* ...
## prints messages only from project base operations
DEBUG=cypress:server:project ...
This allows you to isolate the problem a little better
Log sources
Cypress is built from multiple packages, each responsible for its own logging: server, reporter, driver, command line, etc. Each package writes debug logs under a different source. Here are a few common log sources and when you might want to enable them
Set DEBUG to value | To enable debugging |
|---|---|
cypress:* | ALL modules |
cypress:cli* | Top-level command line parsing and binary installation |
cypress:server:args | Incorrect parsed command line arguments |
cypress:data-context:sources:* | Not finding the expected project data |
cypress:server:project | Opening the project |
cypress:server:browsers* | Finding installed browsers |
cypress:launcher:* | Launching the found browser |
cypress:server:video | Video recording |
cypress:network:* | Adding network interceptors |
cypress:net-stubbing:* | Network interception in the proxy layer |
cypress:server:reporter | Problems with test reporters |
cypress:server:preprocessor | Processing specs |
cypress:server:socket-e2e | Watching spec files |
cypress:server:task | Invoking the cy.task() command |
cypress:server:socket-base | Debugging cy.request() command |
cypress:webpack | Bundling specs using webpack |
cypress:server:fixture | Loading fixture files |
cypress:server:record:ci-info | Git commit and CI information when recording to Cypress Cloud |
You can combine several areas together using the comma character. For example, to debug specs not being found, use:
## see how CLI arguments were parsed
## and how Cypress tried to locate spec files
DEBUG=cypress:cli,cypress:data-context:sources:FileDataSource,cypress:data-context:sources:ProjectDataSource npx cypress run --spec ...
You can also exclude a log source using the - character. For example, to see all
cypress:server* messages without noisy browser messages use:
DEBUG=cypress:server*,-cypress:server:browsers* npx cypress run
Debug log depth
Sometimes the logged object has deeply nested properties and is shown as
[Object] instead of the full serialization.
DEBUG=cypress:server:socket-base npx cypress run
cypress:server:socket-base backend:request { eventName: 'http:request', args:
[ { url: 'http://localhost:7065/echo', method: 'POST', body: [Object], auth: [Object],
json: true, encoding: 'utf8', gzip: true, timeout: 30000, followRedirect: true,
failOnStatusCode: true, retryOnNetworkFailure: true,
retryOnStatusCodeFailure: false } ] } +5ms
You can increase the printed object depth using the DEBUG_DEPTH environment
variable
DEBUG=cypress:server:socket-base DEBUG_DEPTH=3 npx cypress run
cypress:server:socket-base backend:request { eventName: 'http:request', args:
[ { url: 'http://localhost:7065/echo', method: 'POST', body: { text: 'ping!' },
auth: { username: 'jane.lane', password: 'password123' }, json: true, encoding: 'utf8',
gzip: true, timeout: 30000, followRedirect: true, failOnStatusCode: true,
retryOnNetworkFailure: true, retryOnStatusCodeFailure: false } ] } +4ms
3rd party modules
Some 3rd party modules like
@cypress/request output additional log
messages by inspecting the NODE_DEBUG environment variable. For example to
debug the network interception and the requests made by the @cypress/request module
use:
DEBUG=cypress:net-stubbing:server:intercept-request \
NODE_DEBUG=request npx cypress run
Debug logs in the browser
If the problem is seen during cypress open you can print debug logs in the
browser too. Open the browser's Developer Tools and set a localStorage
property:
localStorage.debug = 'cypress*'
// to disable debug messages
delete localStorage.debug
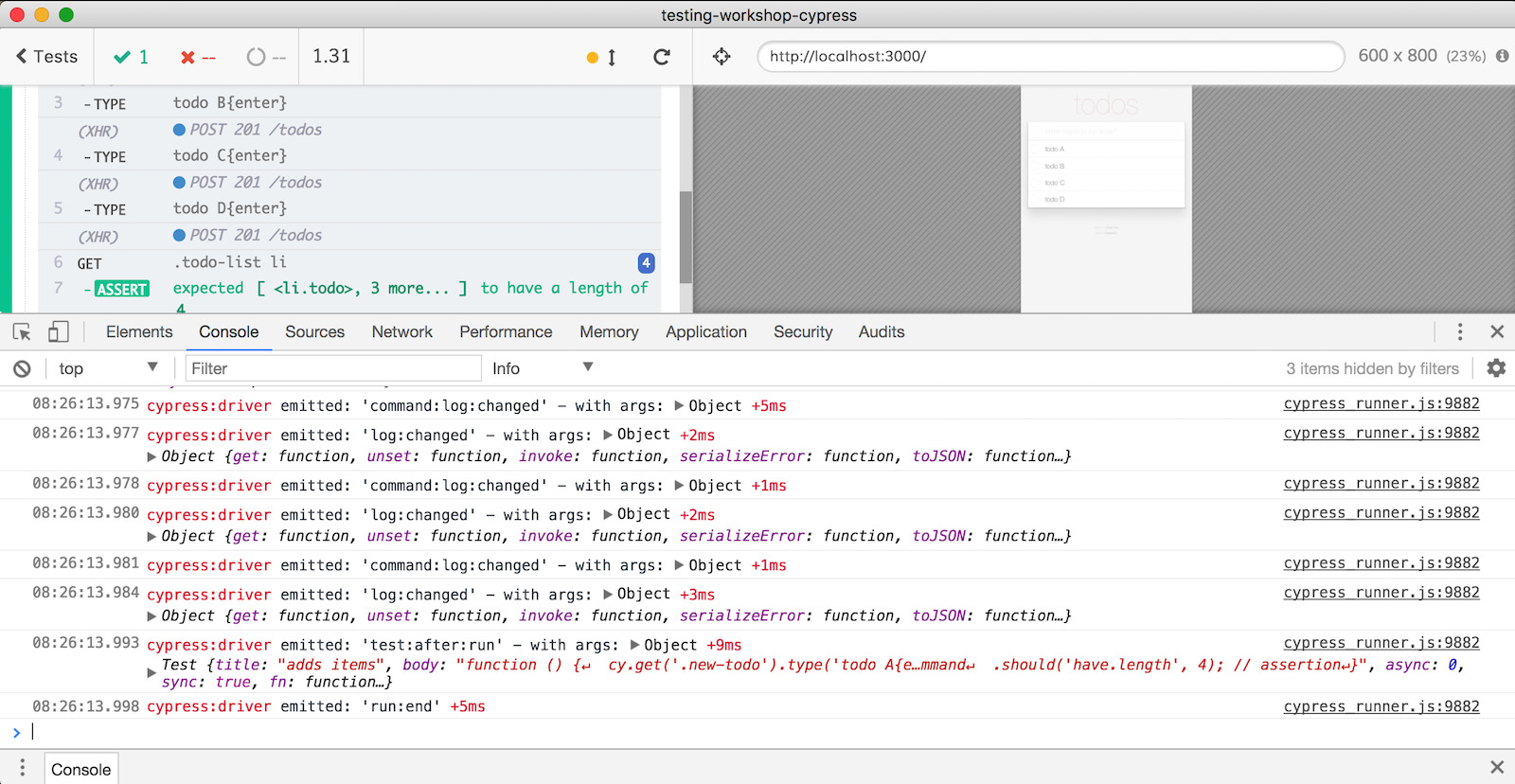
Reload the browser and turn on 'Verbose' logs to see debug messages within the Developer Tools console. You will only see the cypress:driver package logs that run in the browser, as you can see below.
Log memory and CPU usage
You can tell Cypress to log out a summary of the memory and CPU usage of itself
and any subprocesses at a regular interval by enabling the
cypress:server:util:process_profiler debug stream, like so:
DEBUG=cypress:server:util:process_profiler npx cypress run
(See Print DEBUG Logs above for hints on setting
the DEBUG environment variable in a non-POSIX Windows terminal.)
In the resulting output, processes are grouped by their name.
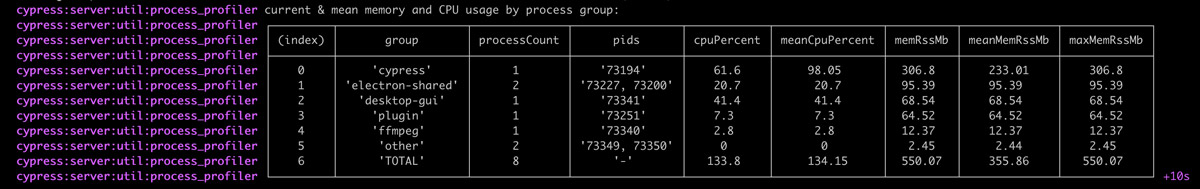
By default, process information is collected, summarized and is printed once
every 10 seconds. You can override this interval by setting the
CYPRESS_PROCESS_PROFILER_INTERVAL environment variable to the desired interval
in milliseconds.
You can also obtain more detailed per-process information by enabling the
verbose cypress-verbose:server:util:process_profiler debug stream.
Disable the Command Log
In some cases the Command Log, responsible for displaying test commands, assertions, and statuses in the Cypress Test Runner, may cause performance issues resulting in slower tests or the browser crashing.
In order to isolate these issues, you can hide the Command Log by passing the
environment variable below during cypress open or cypress run.
CYPRESS_NO_COMMAND_LOG=1 cypress run
You can also hide the entire Cypress Runner UI in cypress run by passing the --no-runner-ui command line flag.
npx cypress run --no-runner-ui
With this variable set, Cypress will skip rendering the Command Log entirely, and perform none of the usual DOM updates to display information about commands and statuses as the test runs.
Note: With this variable set, screenshots and videos will not include the Command Log.
Download specific Chrome version
The Chrome browser is evergreen - meaning it will automatically update itself, sometimes causing a breaking change in your automated tests. You can use the information in Download Chromium to download a specific released version of Chromium for every platform.
Specific Issues
Launching browsers
Cypress attempts to automatically find installed Chrome versions for you. However, probing for browsers across different environments can be error-prone. If Cypress cannot find a browser but you know you have it installed, there are ways to ensure that Cypress can "see" it.
--browser command line argumentYou can also supply the --browser command line argument to launch a browser
from a known filesystem path to bypass browser auto detection.
See 'Launching Browsers' for more information
You can see the full list of found browsers and their properties within the resolved configuration in the Settings tab of Cypress.
Another way to log what is found by Cypress is to run Cypress with the
DEBUG environment variable set to cypress:launcher:*. This
will print information about the found browsers and their properties to the
terminal.
Tip: use the cypress info command to see all locally detected browsers.
Mac
On Mac, Cypress attempts to find installed browsers by their bundle identifier. If this does not succeed, it will fall back to the Linux browser detection method.
| Browser Name | Expected Bundle Identifier | Expected Executable Path |
|---|---|---|
chrome | com.google.Chrome | /Applications/Google Chrome.app/Contents/MacOS/Google Chrome |
chrome:beta | com.google.Chrome.beta | /Applications/Google Chrome Beta.app/Contents/MacOS/Google Chrome Beta |
chrome:canary | com.google.Chrome.canary | /Applications/Google Chrome Canary.app/Contents/MacOS/Google Chrome Canary |
chrome-for-testing | com.google.chrome.for.testing | /Applications/Google Chrome for Testing.app/Contents/MacOS/Google Chrome for Testing |
chromium | org.chromium.Chromium | /Applications/Chromium.app/Contents/MacOS/Chromium |
firefox | org.mozilla.firefox | /Applications/Firefox.app/Contents/MacOS/firefox |
firefox:dev | org.mozilla.firefoxdeveloperedition | /Applications/Firefox Developer Edition.app/Contents/MacOS/firefox |
firefox:nightly | org.mozilla.nightly | /Applications/Firefox Nightly.app/Contents/MacOS/firefox |
edge | com.microsoft.Edge | /Applications/Microsoft Edge.app/Contents/MacOS/Microsoft Edge |
edge:beta | com.microsoft.Edge.Beta | /Applications/Microsoft Edge Beta.app/Contents/MacOS/Microsoft Edge Beta |
edge:canary | com.microsoft.Edge.Canary | /Applications/Microsoft Edge Canary.app/Contents/MacOS/Microsoft Edge Canary |
edge:dev | com.microsoft.Edge.Dev | /Applications/Microsoft Edge Dev.app/Contents/MacOS/Microsoft Edge Dev |
For the current list, see packages/launcher files.
Note: chrome-for-testing and chromium typically require the downloaded application file to be manually moved to the /Applications folder to be auto-detected.
Linux
On Linux, Cypress scans your PATH for a number of different binary names. If
the browser you are trying to use does not exist under one of the expected
binary names, Cypress will not be able to find it.
| Browser Name | Expected Binary Name(s) |
|---|---|
chrome | google-chrome, chrome, or google-chrome-stable |
chrome:beta | google-chrome-beta |
chrome:canary | google-chrome-canary |
chrome-for-testing | chrome |
chromium | chromium-browser or chromium |
firefox | firefox |
firefox:dev | firefox-developer-edition, firefox |
firefox:nightly | firefox-nightly, firefox-trunk |
edge | edge, microsoft-edge |
edge:beta | edge-beta, microsoft-edge-beta |
edge:canary | edge-canary, microsoft-edge-canary |
edge:dev | edge-dev, microsoft-edge-dev |
These binary names should work for most Linux distributions. If your distribution packages browsers under a different binary name, you can add a symlink using the expected binary name so that Cypress can detect it.
For example, to create a symlink for the chrome-for-testing browser:
sudo ln -s /path/to/binary/chrome /usr/local/bin/chrome
Note: chrome-for-testing and chromium typically require the binary to be manually added to the PATH or a symlink created to be auto-detected.
Windows
On Windows, Cypress scans the following locations to try to find each browser:
| Browser Name | Expected Executable Path |
|---|---|
chrome | C:/Program Files/Google/Chrome/Application/chrome.exe, C:/Program Files (x86)/Google/Chrome/Application/chrome.exe |
chrome:beta | C:/Program Files/Google/Chrome Beta/Application/chrome.exe, C:/Program Files (x86)/Google/Chrome Beta/Application/chrome.exe |
chrome:canary | %APPDATA%/Local/Google/Chrome SxS/Application/chrome.exe |
chrome-for-testing | C:/Program Files/Google/Chrome for Testing/chrome.exe, C:/Program Files (x86)/Google/Chrome for Testing/chrome.exe |
chromium | C:/Program Files/Google/chrome-win/chrome.exe, C:/Program Files/Google/Chromium/chrome.exe, C:/Program Files (x86)/Google/chrome-win32/chrome.exe, C:/Program Files (x86)/Google/Chromium/chrome.exe |
firefox | C:/Program Files/Mozilla Firefox/firefox.exe, C:/Program Files (x86)/Mozilla Firefox/firefox.exe, %APPDATA%/Local/Mozilla Firefox/firefox.exe |
firefox:dev | C:/Program Files/Firefox Developer Edition/firefox.exe, C:/Program Files (x86)/Firefox Developer Edition/firefox.exe, %APPDATA%/Local/Firefox Developer Edition/firefox.exe |
firefox:nightly | C:/Program Files/Firefox Nightly/firefox.exe, C:/Program Files (x86)/Firefox Nightly/firefox.exe, %APPDATA%/Local/Firefox Nightly/firefox.exe |
edge | C:/Program Files (x86)/Microsoft/Edge/Application/msedge.exe |
edge:beta | C:/Program Files (x86)/Microsoft/Edge Beta/Application/msedge.exe |
edge:canary | %APPDATA%/Local/Microsoft/Edge SxS/Application/msedge.exe |
edge:dev | C:/Program Files (x86)/Microsoft/Edge Dev/Application/msedge.exe |
For the current list, see packages/launcher files.
To make a browser installed at a different path be auto-detected, create a
symlink using mklink in the location that Cypress expects to find your
browser.
For example, to create a symlink for the chrome-for-testing browser:
mklink /d "C:\Program Files\Google\Chrome for Testing" "C:\path\to\chrome\executable\folder"
Note: chrome-for-testing and chromium typically require the downloaded folder to either be moved and renamed to the location mentioned above or a symlink created as described above to be auto-detected.
Occasionally Cypress will have issues detecting the type of browser in Windows environments. To manually detect the browser type, append the browser type to the end of the path:
cypress open --browser C:/User/Application/browser.exe:chrome
Hacking on Cypress
If you want to dive into Cypress and edit the code yourself, you can do that. The Cypress code is open source and licensed under an MIT license. There are a few tips on getting started that we've outlined below.
Contribute
If you'd like to contribute directly to the Cypress code, we'd love to have your help! Please check out our contributing guide to learn about the many ways you can contribute.
Run Cypress by itself
Cypress comes with an npm CLI module that parses the arguments, starts the Xvfb server (if necessary), and then opens Cypress.
Some common situations on why you would want to run Cypress by itself are to:
- debug Cypress not starting or hanging
- debug problems related to the way CLI arguments are parsed by the npm CLI module
Here is how you can launch Cypress directly without the npm CLI module. First, find where Cypress binary versions are installed using the cypress cache path and cypress cache list commands.
An example on a Linux machine shows:
$ npx cypress cache path
/home/<username>/.cache/Cypress
$ npx cypress cache list
| version | last used |
|---|---|
| 13.15.0 | 12 days ago |
You can replace the Linux /home/<username> directory with the ~ character in the following example steps.
Second, try a smoke test that verifies that the application has all its required dependencies present on the host machine. Ignore the warning about running the Cypress binary directly.
$ ~/.cache/Cypress/13.15.0/Cypress/Cypress --smoke-test --ping=101
DevTools listening on ws://127.0.0.1:39737/devtools/browser/162ad33c-294b-460b-812e-cc317907ac86
It looks like you are running the Cypress binary directly.
This is not the recommended approach, and Cypress may not work correctly.
Please install the cypress NPM package and follow the instructions here:
https://on.cypress.io/install-cypress
101
If there is a missing dependency, the smoke test will fail to run and the application will print an error message referring to Linux Prerequisites. Follow the instructions to ensure all required dependencies are installed.
To troubleshoot missing shared library dependencies on Linux, use the ldd command on the Cypress binary.
A missing dependency should be identified with "not found" in the output.
ldd ~/.cache/Cypress/13.15.0/Cypress/Cypress
linux-vdso.so.1 (0x00007ffe0e7db000)
libffmpeg.so => /home/<username>/.cache/Cypress/13.15.0/Cypress/libffmpeg.so (0x0000774bc7a00000)
libdl.so.2 => /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libdl.so.2 (0x0000774bd26d0000)
libpthread.so.0 => /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libpthread.so.0 (0x0000774bd26cb000)
libgobject-2.0.so.0 => /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libgobject-2.0.so.0 (0x0000774bd2668000)
libglib-2.0.so.0 => /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libglib-2.0.so.0 (0x0000774bd251f000)
libgio-2.0.so.0 => /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libgio-2.0.so.0 (0x0000774bc7e30000)
libnss3.so => not found
...
Tip: If you are having problems with dependencies, use a Cypress Docker image. These have all Cypress dependencies pre-installed.
On Ubuntu 24.04 you may receive a fatal error including the text FATAL:setuid_sandbox_host.cc due to added security in this version of Ubuntu.
Refer to the Ubuntu 24.04 Release notes in the section Unprivileged user namespace restrictions and apply one of the workarounds to disable unprivileged user namespace restrictions for the entire system, either for one boot or persistently, as described.
Alternatively you can follow the instructions in the error message similar to:
You need to make sure that
/home/<username>/.cache/Cypress/13.15.0/Cypress/chrome-sandboxis owned by root and has mode 4755.
and execute for example:
sudo chown root:root ~/.cache/Cypress/13.15.0/Cypress/chrome-sandbox
sudo chmod +4755 ~/.cache/Cypress/13.15.0/Cypress/chrome-sandbox
You can see the Electron verbose log messages by setting an environment variable ELECTRON_ENABLE_LOGGING.
Note: Verbose Electron logging might show warnings that still allow Cypress to work normally. For example, the following Bluetooth related warning can be ignored:
WARNING:bluez_dbus_manager.cc
ELECTRON_ENABLE_LOGGING=true ~/.cache/Cypress/13.15.0/Cypress/Cypress --smoke-test --ping=101
DevTools listening on ws://127.0.0.1:33161/devtools/browser/1f8a2d15-ea42-403f-8eb4-757f1a9d0b25
[3959:1005/201139.970068:WARNING:bluez_dbus_manager.cc(247)] Floss manager not present, cannot set Floss enable/disable.
It looks like you are running the Cypress binary directly.
This is not the recommended approach, and Cypress may not work correctly.
Please install the cypress NPM package and follow the instructions here:
https://on.cypress.io/install-cypress
101
You can also see Cypress debug logs by setting an
environment variable DEBUG=cypress:*.
$ DEBUG=cypress:* ~/.cache/Cypress/13.15.0/Cypress/Cypress --smoke-test --ping=101
cypress:snapshot:info Caching 3374, defining 4217 modules! Using cache +0ms
cypress:snapshot:debug initializing packherd require +0ms
cypress:server:performance-benchmark elapsed time at v8-snapshot-startup-time: 204.65ms +0ms
cypress:server:appdata path: /home/<username>/.config/Cypress/cy/production/browsers +0ms
cypress:server appending default switches for electron: [
cypress:server { name: '--test-type' },
...
cypress:server { name: '--enable-precise-memory-info' }
cypress:server ] +0ms
cypress:server:cypress starting cypress with argv [ '/home/<username>/.cache/Cypress/13.15.0/Cypress/Cypress', '--smoke-test', '--ping=101' ] +0ms
...
cypress:server:cypress running Electron currently +13ms
101
cypress:server:cypress about to exit with code 0 +18ms
cypress:server:browsers browsers.kill called with no active instance +0ms
If the smoke test does not show a specific error yet crashes, try printing the Electron crash stack to maybe pinpoint the problem better:
ELECTRON_ENABLE_STACK_DUMPING=1 npx cypress verify
...
Received signal 11 SEGV_MAPERR ffffffb27e8955bb
#0 0x55c6389f83d9 (/home/<username>/.cache/Cypress/13.15.0/Cypress/Cypress+0x35d13d8)
r8: 0000000000000000 r9: 00007ffcf0387c80 r10: 00007ffcf0387bd8 r11: 000000000000000e
r12: 00007ffcf0387d2c r13: 00007f3ea737b720 r14: ffffffb27e89558b r15: 00007f3ea8974200
di: 0000000000000000 si: 0000000000000020 bp: 0000000000000000 bx: 0000004f2f375580
dx: 0000000000000001 ax: 0000000000000030 cx: 0000000000000001 sp: 00007ffcf0387d00
ip: 00007f3ea89582dd efl: 0000000000010246 cgf: 002b000000000033 erf: 0000000000000005
trp: 000000000000000e msk: 0000000000000000 cr2: ffffffb27e8955bb
[end of stack trace]
Calling _exit(1). Core file will not be generated.
Patch Cypress
Cypress comes with an npm CLI module that parses the arguments, starts the Xvfb server (if necessary), and then opens Cypress.
If you're encountering a bug in the current version of Cypress, you can implement a temporary fix by patching Cypress in your own project. Here is an example of how to do this.
- Install patch-package.
- Add a patch step to your CI configuration after installing your npm packages.
- run: npm ci
- run: npx patch-package
Alternatively, you can apply the patch during a post-install phase. In your
package.json, for example, you could add the following:
{
"scripts": {
"postinstall": "patch-package"
}
}
- Edit the line causing the problem in your local node_modules folder within
node_modules/cypress. - Run the
npx patch-package cypresscommand. This command will create a new file named after the current Cypress version, for example,patches/cypress+13.15.0.patch.
npx patch-package cypress
patch-package 8.0.0
• Creating temporary folder
• Installing cypress@13.15.0 with npm
• Diffing your files with clean files
✔ Created file patches/cypress+13.15.0.patch
💡 cypress is on GitHub! To draft an issue based on your patch run
npx patch-package cypress --create-issue
- Commit the new
patchesfolder to git.
If you find a patch for an error, please add a comment to the relevant Cypress GitHub issue explaining your workaround. It can help us release an official fix faster. Alternatively you can use the following command to create a new issue based on your patch contents.
npx patch-package cypress --create-issue