Proxy Configuration
Cypress needs Internet access to work. Many companies require the use of a corporate proxy to access the Internet. If your company does this, many functions of Cypress will not work until you've configured Cypress to use your proxy:
- Cypress won't be able to load web pages besides
localhost. - Cypress won't be able to warn you if your baseUrl isn't available.
- Cypress won't be able to connect to Cypress Cloud to log in or record test runs.
npm install cypressmay fail while downloading the Cypress binary.
If you are experiencing any or all of these issues, you may need to configure Cypress with your proxy. Instructions are available for macOS, Linux, and Windows.
Proxy Auto-Configuration (PAC) files are not currently supported. If your organization uses a PAC file, contact a network administrator to ask what HTTP proxy you should be using to access the general Internet, then use that proxy with Cypress.
SOCKS proxies are not currently supported. A workaround is to set up an HTTP proxy locally that points to your SOCKS proxy, then using that HTTP proxy with Cypress. Read more about forwarding an HTTP proxy through SOCKS.
Set a proxy on Linux or macOS
To set your proxy on Linux or macOS, run the following command in a terminal before running Cypress:
export HTTP_PROXY=http://my-company-proxy.com
You can also set NO_PROXY to bypass the proxy for certain domains (by default,
only localhost will be bypassed):
export NO_PROXY=localhost,google.com,apple.com
To make these changes permanent, you can add these commands to your shell's
~/.profile (~/.zsh_profile, ~/.bash_profile, etc.) to run them on every
login.
Set a proxy on Windows
When starting up after being installed, Cypress will attempt to load the proxy configured in the Windows registry by default. Learn how to set your proxy settings system-wide in Windows.
When downloading Cypress for the first time, the cypress command line tool
does not read proxy settings from the Windows registry. If you need to
configure a proxy for the installation to work, you must set the appropriate
environment variables as described below.
You can also set proxy environment variables before running Cypress to override
the Windows registry. This is also the only way to define a proxy for
cypress install. In Command Prompt, defining the required environment
variables looks like this:
set HTTP_PROXY=http://my-company-proxy.com
To accomplish the same thing in PowerShell:
$env:HTTP_PROXY = "http://my-company-proxy.com"
To save the HTTP_PROXY variable and use your proxy for all new shells, use
setx:
setx HTTP_PROXY http://my-company-proxy.com
Proxy environment variables
This section refers to your operating system's environment variables, not Cypress environment variables
Cypress automatically reads from your system's HTTP_PROXY environment variable
and uses that proxy for all HTTP and HTTPS traffic. If an HTTPS_PROXY
environment variable is set, HTTPS traffic will use that proxy instead.
To bypass the proxy for certain domains, a NO_PROXY environment variable can
be set to a comma-separated list of domain names to not proxy traffic for. By
default, traffic to localhost will not be proxied. To make Cypress send
traffic for localhost through the proxy, pass <-loopback> in NO_PROXY.
If an uppercase and a lowercase version of the proxy settings are supplied (for
example, HTTP_PROXY and http_proxy are both set), the lowercase variable
will be preferred.
Using a custom certificate authority (CA)
This section refers to npm config variables and node environment variables, not Cypress environment variables
Cypress needs to be able to authenticate properly when communicating to
Cypress Cloud. When connecting through a proxy,
oftentimes a self signed certificate is used as a CA. In order to handle this
configuration, Cypress automatically reads from npm config's
cafile and
ca options and the
NODE_EXTRA_CA_CERTS
node environment variable.
To mimic the behavior of npm and node, Cypress looks at cafile first and then
ca and uses the corresponding certificate(s) as a replacement for the CA. For
example, to use the CA at /home/person/certs/ca.crt, add the following to your
.npmrc:
cafile=/home/person/certs/ca.crt
If neither cafile nor ca are set, Cypress looks at the system environment
variable NODE_EXTRA_CA_CERTS and uses the corresponding certificate(s) as an
extension for the trusted CA.
Note that the npm config is used as a replacement, and the node environment variable is used as an extension.
View, unset, and set environment variables
In order to properly configure your proxy configuration, it can be helpful to know how to view currently set environment variables, unset unwanted environment variables, and set environment variables depending on your operating system.
Linux or macOS
Set an environment variable for the current session
export SOME_VARIABLE=some-value
Unset an environment variable
unset SOME_VARIABLE
echo will print nothing after unset:
echo $SOME_VARIABLE
See all the currently set environment variables
Avoid in CI environments
Do not print environment variables in CI runs where logs are captured and stored, as this can expose sensitive information like passwords, API keys, or tokens that may be stored in environment variables.
Print all env vars:
env
Print environment variables with proxy (case insensitive) in the name:
env | grep -i proxy
Windows
Setting environment variables in Windows is different depending on if you're using command prompt or PowerShell.
Set an environment variable for current session
Command prompt:
set SOME_VARIABLE=some-value
PowerShell:
$env:SOME_VARIABLE = "some-value"
Set environment variable globally for all future sessions
setx SOME_VARIABLE some-value
Unset an environment variable in the current session
Command prompt:
set SOME_VARIABLE=
PowerShell:
Remove-Item Env:\SOME_VARIABLE
See all currently set environment variables
Command prompt:
set
PowerShell:
Get-ChildItem Env:
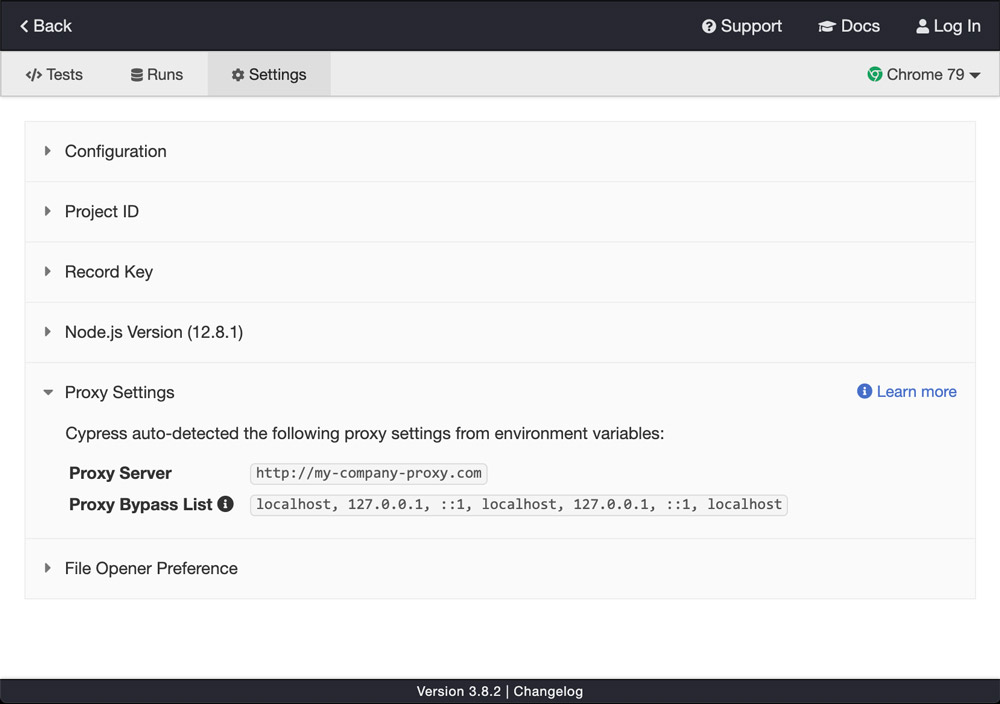
View proxy settings in Cypress
Your current proxy settings can be viewed from within Cypress. Follow these steps:
- Open up your project in Cypress via
cypress open. - Click the "Settings" tab.
- Click the "Proxy Settings" section to expand it and view the proxy settings that Cypress is currently using.