Identify coverage gaps
Understanding your application's test coverage is crucial for ensuring quality and reliability. Cypress's UI Coverage tool provides insights into which parts of your application are tested and highlights untested areas. This guide will help you get started with UI Coverage to identify and address coverage gaps effectively.
Run Tests
To identify coverage gaps, you need to first run and record Cypress tests to the Cloud. If you're new to Cypress, refer to the Cypress documentation to get started with writing tests.
Example: Automated Sitemap-Based Testing
If your project lacks existing Cypress tests, a common approach is to understand test coverage from a sitemap or an array of target URLs. These URLs can be used to perform light interactions and capture the initial gaps in testing. Below is an example of how to automate this process by using a sitemap:
describe('UI Coverage Scan', () => {
it('Checks ui coverage with the sitemap.xml', () => {
cy.request('https://<YOUR_WEBSITE>/sitemap.xml').then((response) => {
const xmlString = response.body
const parser = new DOMParser()
(loc) => loc.textContent
})
Cypress._.each(URLs, (URL) => {
cy.visit(URL)
})
})
})
Review Coverage Reports
Once your tests have recorded to Cypress Cloud, you can analyze the coverage reports to identify gaps. Click on the runs in your project in Cypress Cloud to access the UI Coverage reports. This report provides a visual representation of your application's test coverage, highlighting tested and untested elements.
Overall Score
The first metric to review is the overall coverage score. This score is calculated by comparing the number of tested elements to the total number of interactive elements in your application. A higher score indicates better coverage, while a lower score indicates areas that need additional testing. The score will display on the runs page and within individual runs.
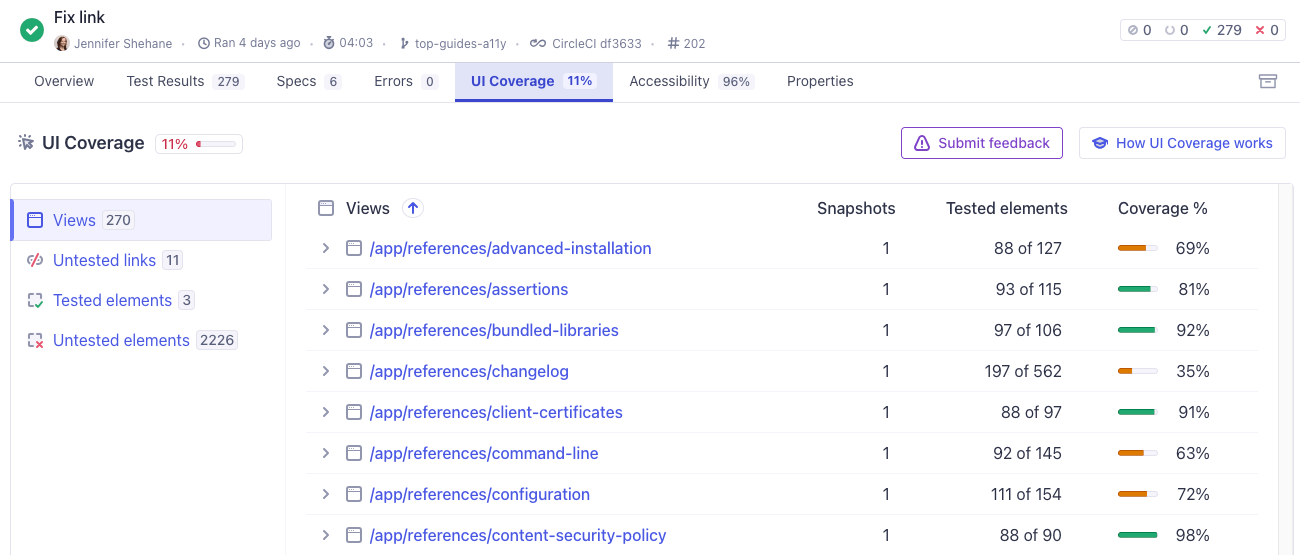
Views
Within a run's UI Coverage tab, you'll find a Views section. Views represent different pages or components of your application. Each view in the list displays the URL or component path, the number of snapshots, the number of untested and tested elements in that view, and the coverage score.
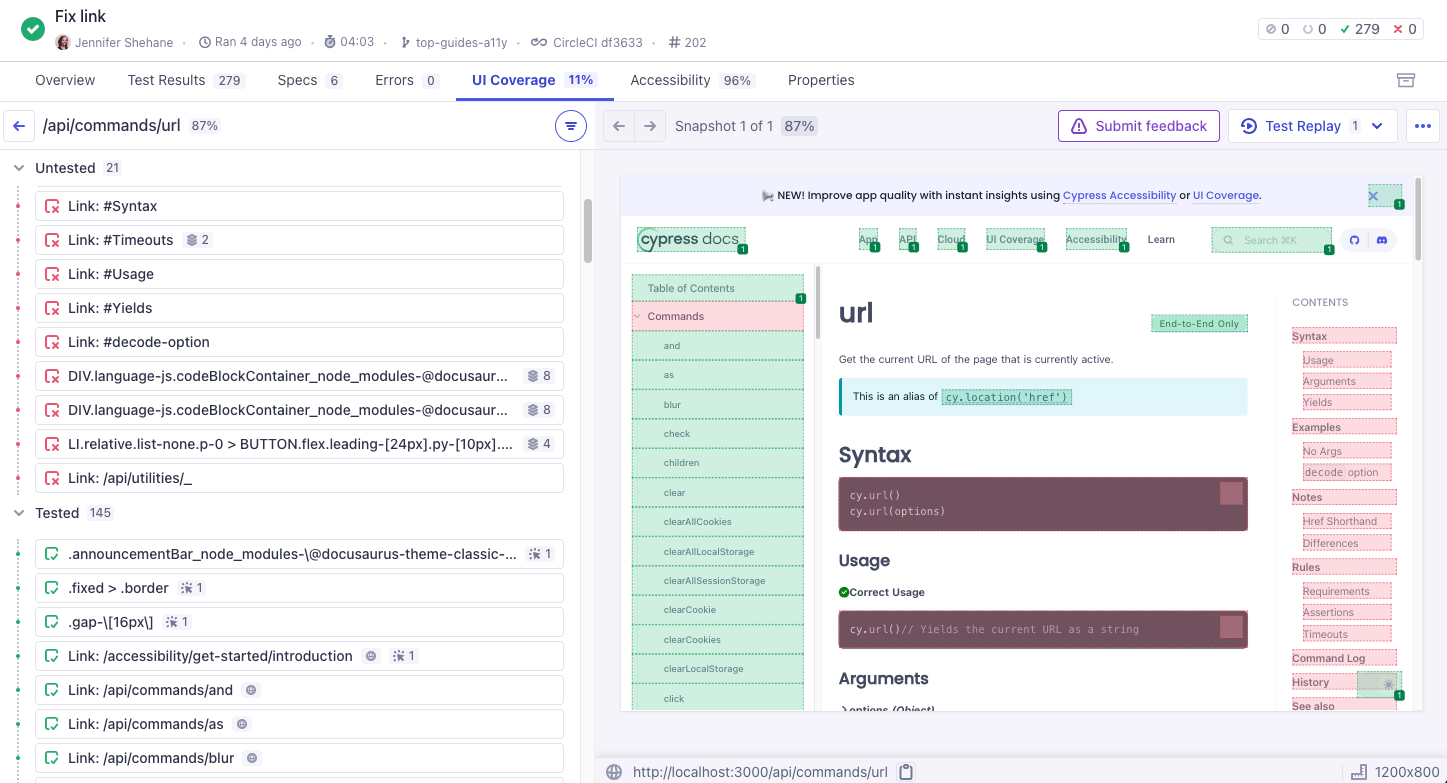
View Drilldown
Clicking into a view shows a detailed breakdown of the tested and untested elements within that view. You can use this information to inspect the DOM snapshot of the element using your browser's developer tools and understand the context of any coverage gaps. The view includes:
- Untested Elements: A list of interactive elements that were not interacted with during the test run.
- Tested Elements: A list of interactive elements that were interacted with during the test run.
- DOM Snapshot: A full-page, inspectable DOM snapshot of the view as it appeared during the test run. Tested elements highlight as green, while untested elements highlight as red.
- Snapshot Navigation: Navigate between snapshots to see the state of the view at different points during the test run.
- Snapshot Coverage Score: The coverage score for the specific snapshot based on the number of tested elements.
- Test Replay: A link to the Test Replay for the specific snapshot.
- URL and Viewport size: Metadata for the view.
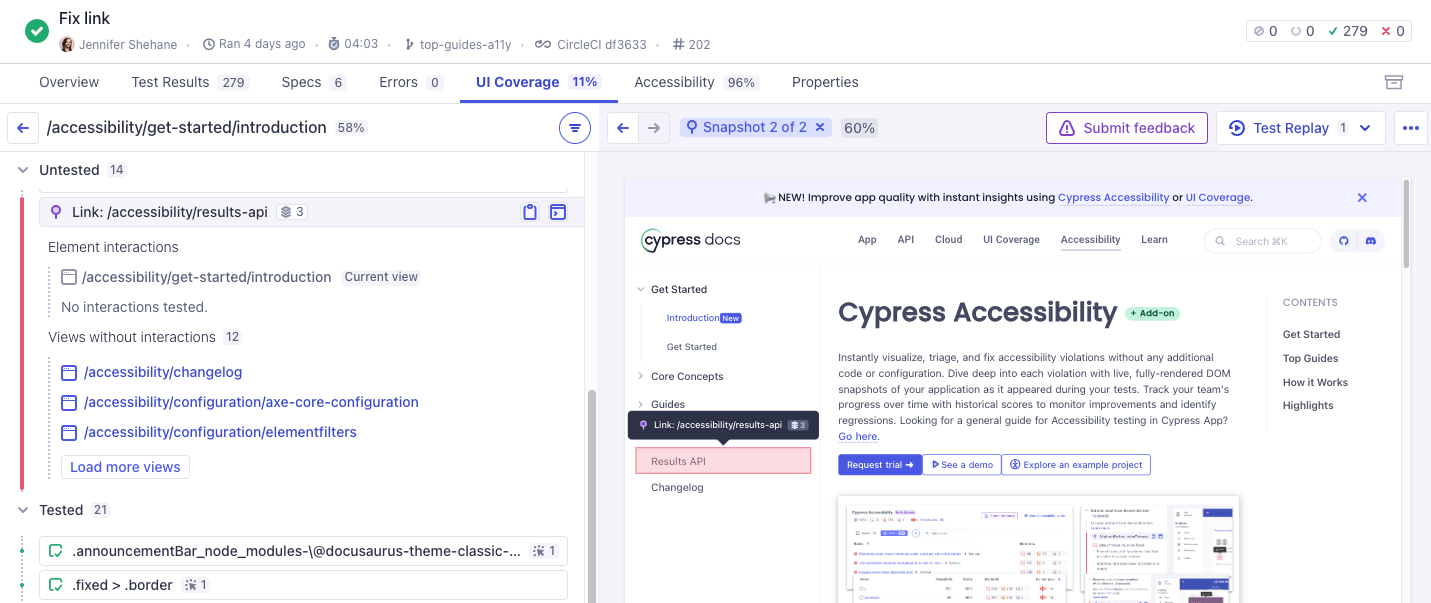
Untested links
In the UI Coverage tab, the Untested links section lists all the links not interacted with during the test run. This can help you identify pages of your application that are not being visited and tested. Use this to identify unvisited pages and prioritize testing.
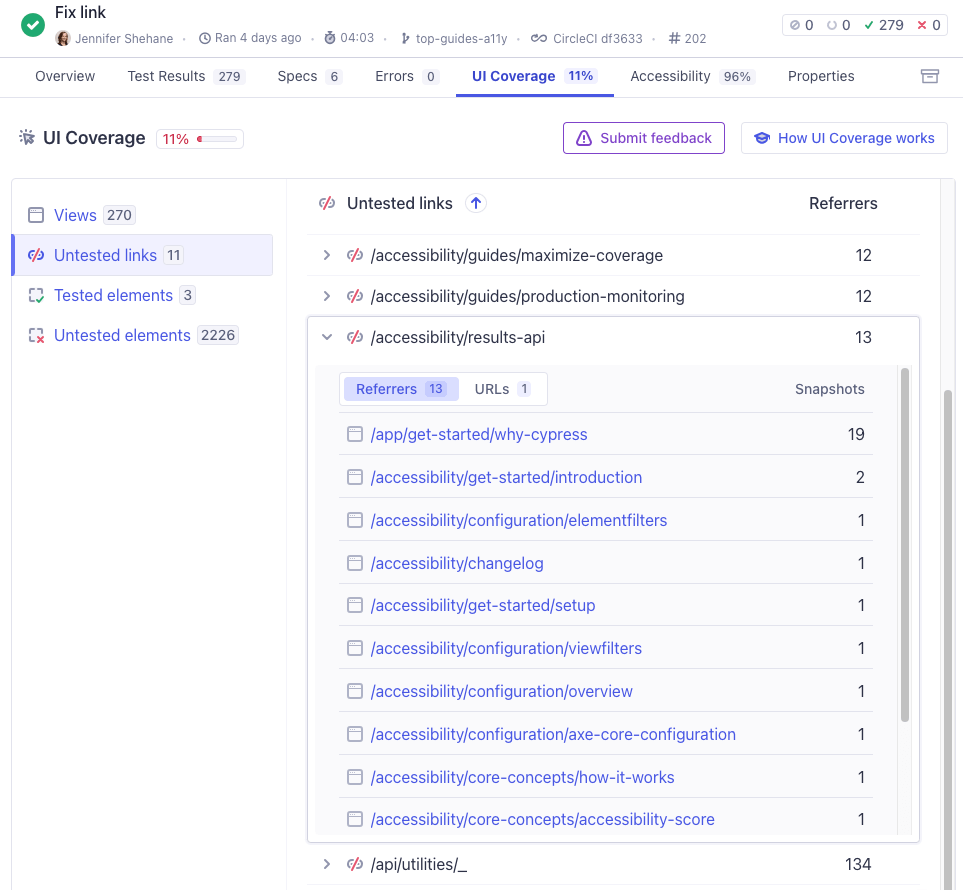
Referrer Drilldown
Clicking a referrer link redirects you to the referrer's view, where the untested link is highlighted in red.
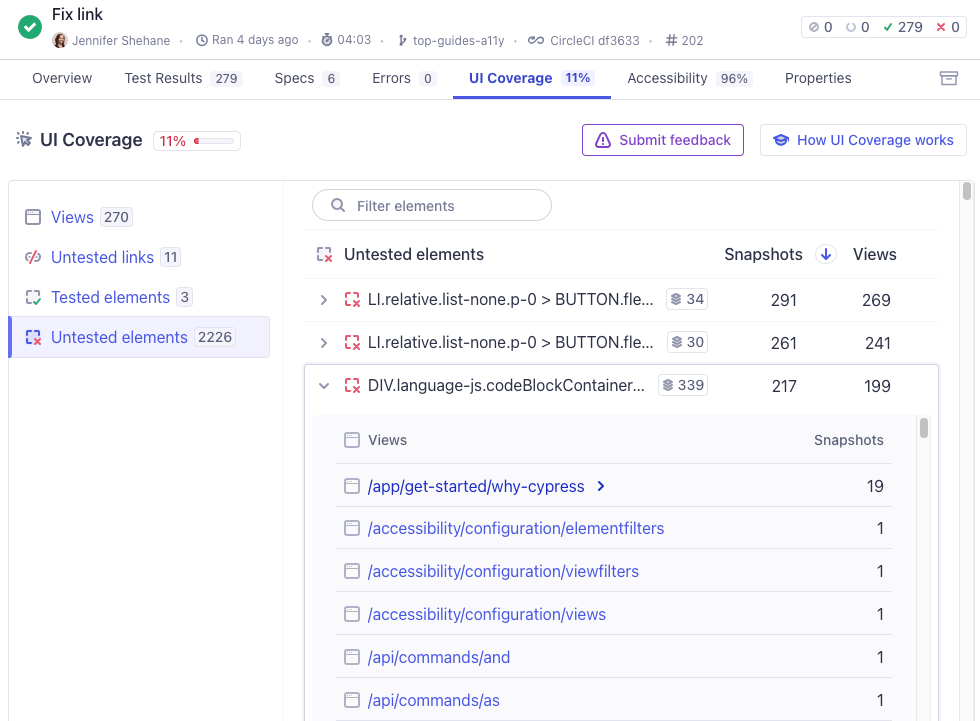
Untested elements
The Untested Elements section in the UI Coverage tab lists all interactive elements not interacted with during the test run. This can help you identify specific elements that are not being tested across views. Use this information to prioritize testing for these elements.
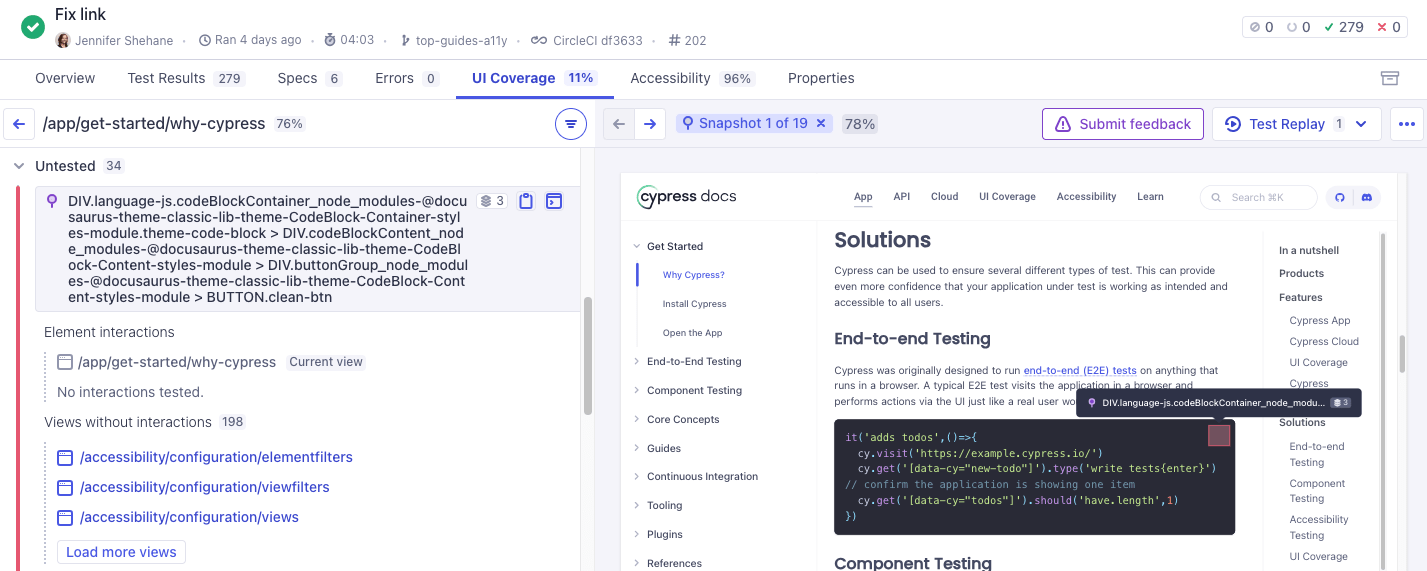
View Drilldown
Clicking into an untested element's view shows a detailed breakdown of the element, including the element's selector, the number of times the element was interacted with, and the views without interactions. You can use this information to inspect the DOM snapshot of the element using your browser's developer tools and understand the context of any coverage gaps.
Configure UI Coverage
While UI Coverage is designed to work seamlessly out of the box, there are instances where custom configuration may be necessary to address unique application structures, testing requirements, or edge cases. Refer to the Configuration Guide to learn how to customize UI Coverage to address these common needs:
- Filtering: Exclude specific elements or views from coverage reports.
- Element Filters: Exclude specific elements from coverage reports.
- View Filters: Exclude specific views from coverage reports.
- Grouping: Group similar elements together for easier analysis.
- Elements: Specify selectors to uniquely identify elements, even when they lack stable identifiers across snapshots.
- Element Grouping: Group similar elements together for easier analysis.
- Views: Group views together based on defined URL patterns.
- Defining Attribute Patterns: Define patterns for identifying and grouping elements by attributes.
- Attribute Filters: Specify patterns for attributes and their values that should not be used for identifying and grouping elements.
- Significant Attributes: Define selectors to prioritize above the default attributes Cypress uses for the purpose of identification and grouping.
Next Steps
By leveraging these tools and techniques, you can effectively identify test coverage gaps. Next, read our guide on addressing coverage gaps to ensure a robust and reliable application.